Harley Street Sleep Center Facility is now equipped with Capnograph
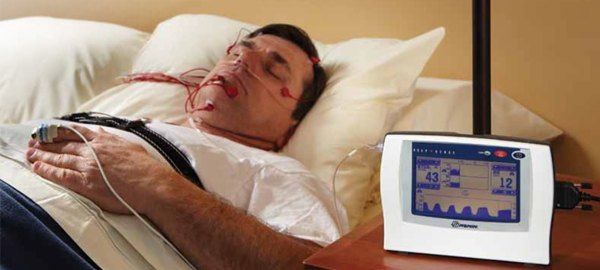 End-tidal CO2 (EtCO2) monitoring, also known as capnography, recently has become a common measurement in sleep studies. When conducting sleep studies, it is important to accurately and consistently measure exhaled CO2 levels in order to reliably assess the quality of ventilation during sleep.
End-tidal CO2 (EtCO2) monitoring, also known as capnography, recently has become a common measurement in sleep studies. When conducting sleep studies, it is important to accurately and consistently measure exhaled CO2 levels in order to reliably assess the quality of ventilation during sleep.
Capnography is potentially useful in monitoring the end-tidal partial pressure of CO2 (PCO2) levels when evaluating a patient for sleep-related hypoventilation. It helps clinicians diagnose sleep breathing disorders hypoventilation syndrome. If hypoventilation in children is not detected and treated promptly it may lead to poor developmental outcomes, and in adults can contribute to increased morbidity and mortality. Capnography has also been reported to be a useful screening tool in obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA).
The Capnograph monitors display a very useful number called EtCO2. End-tidal means “end of breath” measurement which is the CO2 measure at the very end of expiration. The EtCO2 is approximately equal to the arterial blood CO2. Thus it is a non-invasive and convenient way of estimating arterial CO2.


 أنقر هنا
أنقر هنا أنقر هنا
أنقر هنا