DIABETES MELLITUS
DIABETES MELLITUS
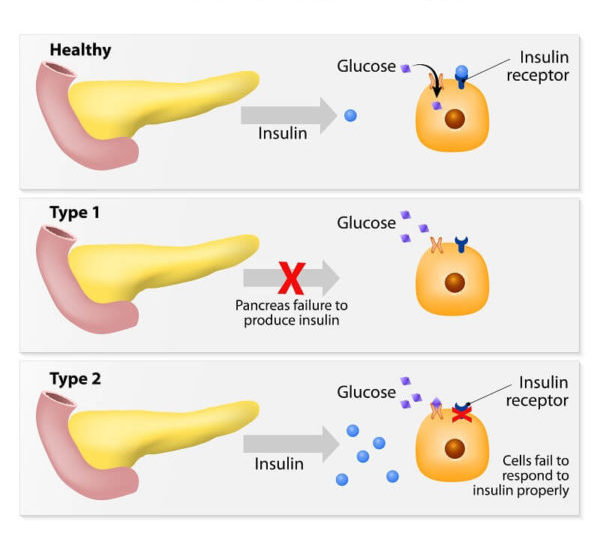
Diabetes is a chronic disease where your blood glucose (or blood sugar), which is your main source of energy, is too high. Insulin, a hormone secreted by the pancreas, helps glucose from food get into your cells to be used for energy. When your body doesn’t make enough or any insulin or doesn’t use insulin well, glucose stays in your blood and doesn’t reach your cells. Too much sugar in the blood can lead to serious health problems.
- Types
- Symptoms
- Risk factors
- Complications
- Prevention
- Treatment
The two main types of diabetes are type 1 and type 2.
Type 1 diabetes often starts during childhood or teen years. Type 2 diabetes, the more common type, can develop at any age but is more common in people older than 40, however it is increasing in children.
Diabetes symptoms depend on how high your blood sugar is. In type 1 diabetes, symptoms are quicker and more severe.
Some of the symptoms include:
- Excess thirst.
- Excess urination.
- Weight loss.
- Fatigue and weakness.
- Blurry vision.
- Recurrent infections.
You are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes with the following:
- Overweight or obesity.
- Age 35 or older.
- Family history of diabetes.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Prediabetes.
- History of gestational diabetes, a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy.
Long-term complications of diabetes develop gradually. The longer you have diabetes and the less controlled your blood sugar the higher the risk of complications.
Possible complications include:
- Heart and blood vessel (cardiovascular) disease.
- Nerve damage from diabetes (diabetic neuropathy).
- Kidney damage from diabetes (diabetic nephropathy).
- Eye damage from diabetes (diabetic retinopathy).
- Foot damage due to nerve damage in the feet or poor blood flow to the feet.
Type 2 diabetes can be prevented:
- Eat healthy foods, lower in fat and calories and higher in fiber.
- Regular physical activity, at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity a week such as brisk walking.
- Lose excess weight, even 7% weight loss can lower the risk of diabetes.
- Sometimes drugs are an option and may lower the risk of type 2 diabetes but a healthy lifestyle is more important.
Treatment of type 1 and type 2 diabetes varies, type 1 is managed by multiple daily insulin injections and type 2 diabetes may be managed by diet alone or in conjunction with tablets or sometimes insulin.
Consult your doctor if you are at risk of diabetes or if you have been diagnosed with diabetes.
ARE YOU CONCERNED?
The only conclusive test for diabetes is a blood test. However, the quiz should give you an indication of whether to seek urgent help, or whether to raise the issue at your next GP appointment.









 أنقر هنا
أنقر هنا أنقر هنا
أنقر هنا