VACCINATION
Immunization & Prevention
Harley Street is committed promoting the health and well-being of our community. As part of our dedication to disease prevention and protection, we are thrilled to offer a comprehensive range of vaccine services. Our team of highly skilled healthcare professionals is here to ensure that you and your loved ones receive the highest standard of care in a safe and welcoming environment.
OUR VACCINATION SERVICES:
At our Clinic, we offer a wide range of vaccines to protect you and your loved ones from various infectious diseases. Some of the most common vaccines (subject to availability) that we provide;
- Shingles Vaccine (Zoster Vaccine):
- Influenza Vaccine (Flu Shot):
- Polio Vaccine:
- Meningococcal(Meningitis) Vaccine:
- Typhoid Vaccine:
- Varicella (Chickenpox) Vaccine:
- Haemophilus influenzae Type b (Hib) Vaccine:
- Pneumococcal Vaccine:
- Measles, Mumps, and Rubella Vaccine (MMR):
- Tetanus, Diphtheria, and Pertussis Vaccine (Tdap):
- Human Papillomavirus Vaccine (HPV):
- Hepatitis A Vaccine:
- Hepatitis B Vaccine:
- Rotavirus Vaccines:
What is Shingles?
Shingles, or herpes zoster, is characterized by blisters and sharp burning nerve pain in the skin caused by reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus, the same virus responsible for chickenpox.
95% of adults aged 50 years or older already have the virus that causes shingles. It can be reactivated at any time and the risk increases as the immune system naturally gets weaker as we grow older.
Risk of shingles increases with age:
Most people only experience shingles once, but it’s possible to get shingles again. In 1 out of 3 people, the dormant varicella zoster virus reactivates and causes shingles. Shingles is caused by a virus that you already carry, so you cannot protect yourself by social distancing.
Shingles Vaccine & Recommendation:
The shingles vaccine, also known as Shingrix (recombinant zoster vaccine), is recommended for individuals aged 50 years and older. It is a one-time vaccination that helps reduce the risk of developing shingles and its associated complications, such as postherpetic neuralgia (PHN).
It is recommended for individuals, even if they have had a previous episode of shingles. It is especially important for those who have a weakened immune system or are at higher risk due to certain medical conditions.
The influenza vaccine, commonly known as the flu shot, is a crucial annual vaccination to protect against the influenza virus.
Recommendation:
Each year, the flu vaccine is formulated to protect against the influenza strains expected to be most prevalent during the upcoming flu season. It is recommended that individuals receive the flu shot annually, ideally before the flu season begins.
The flu shot is especially important for individuals with weakened immune systems, the elderly, and young children. It helps reduce the severity of symptoms and lowers the risk of complications associated with the flu.
Polio, or poliomyelitis, is a highly contagious viral disease caused by the poliovirus. It primarily affects the nervous system, potentially leading to paralysis or even death.
Inactivated Polio Vaccine (IPV):
The inactivated polio vaccine (IPV) is an injectable vaccine that contains inactivated (killed) poliovirus strains. It is the primary form of polio vaccination used in many countries, including the United States. IPV is highly effective in preventing polio infection and its associated complications.
Global Polio Eradication Initiative:
The Global Polio Eradication Initiative (GPEI) is a worldwide effort led by organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) and UNICEF to eradicate polio globally. The GPEI has made significant progress, and today, polio remains endemic in only a few countries.
Importance of Polio Vaccination:
Polio vaccination is vital in preventing the spread of the virus and protecting individuals from the potentially devastating effects of polio infection. By vaccinating against polio, we can contribute to global efforts to eradicate the disease entirely.
Recommendation:
The vaccine is typically administered in a series of doses, starting in infancy and continuing through early childhood.
What is Meningitis ?
Meningitis is an inflammation of the protective membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord. It can be caused by viruses, bacteria, or other infectious agents.
Meningococcal Vaccine:
The meningococcal vaccine protects against meningococcal disease, which is caused by the bacterium Neisseria meningitidis.
Meningococcal vaccines can be divided into two main types: Meningococcal ACWY (quadrivalent) and Meningococcal B (bivalent).
- Meningococcal ACWY Vaccine:
The Meningococcal ACWY vaccine is designed to protect against four common serogroups of the meningococcal bacteria: A, C, W, and Y. These serogroups are responsible for the majority of meningococcal disease cases worldwide. The vaccine is usually administered as a single dose.
Recommendation:
The Meningococcal ACWY vaccine is recommended for individuals at increased risk of meningococcal disease, including adolescents, college students, military recruits, travelers to certain areas with high disease prevalence, individuals with certain medical conditions, and those in close contact with someone infected with meningococcal disease.
- Meningococcal B Vaccine:
The Meningococcal B vaccine is specifically developed to protect against the serogroup B strain of the meningococcal bacteria. Serogroup B has been responsible for a significant proportion of meningococcal disease cases, especially in certain regions. The Meningococcal B vaccine is typically administered as a series of doses.
Recommendation:
The Meningococcal B vaccine can be given to babies and is recommended for individuals at increased risk of meningococcal disease caused by serogroup B, including infants, adolescents, college students, individuals with certain medical conditions, and those in close contact with someone infected with meningococcal disease caused by serogroup B.
Typhoid fever is a bacterial infection caused by the bacterium Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi. It is primarily transmitted through contaminated food and water, particularly in areas with poor sanitation and hygiene practices. Typhoid fever is more common in developing countries, especially in regions of South Asia, Southeast Asia, and parts of Africa.
Typhoid vaccines help to stimulate the immune system to produce antibodies against the S. Typhi bacteria, providing immunity and reducing the risk of developing typhoid fever.
- Inactivated Typhoid Vaccine (Injectable):
This vaccine contains killed or inactivated S. Typhi bacteria. It is administered as an injection and provides protection against typhoid fever.
Recommendation:
Recommended for individuals aged 2 years and older.
Varicella vaccines, also known as chickenpox vaccines, are used to prevent the varicella-zoster virus infection, which causes chickenpox.
Vaccination Types:
There are two main types of varicella vaccines:
- Varicella Vaccine (Varivax):
Varivax is a live attenuated vaccine that contains a weakened form of the varicella-zoster virus. It is administered as a single-dose or two-dose series, depending on the age of the individual.
Recommendation:
The varicella vaccine is typically recommended for children around 12-15 months of age, with a second dose administered between 4-6 years of age. It can also be given to older children, adolescents, and adults who have not been vaccinated or previously had chickenpox.
- Varicella Vaccine (ProQuad):
ProQuad is a combination vaccine that provides protection against varicella (chickenpox), measles, mumps, and rubella. It contains both the varicella vaccine and the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine components.
Recommendation:
ProQuad is typically administered as a two-dose series for children aged 12 months through 12 years. The first dose of ProQuad can be given as early as 12 months of age, and the second dose is usually administered between 4-6 years of age.
The Hib vaccine protects against Haemophilus influenzae type b, a bacterium that can cause meningitis and other severe infections in young children.
The Hib vaccine has greatly reduced the incidence of Hib meningitis in vaccinated populations.
Recommendation:
It is usually administered as a part of routine childhood immunizations, typically starting at two months of age.
The pneumococcal vaccine protects against infections caused by the bacterium Streptococcus pneumoniae, which can lead to pneumonia, meningitis, and bloodstream infections.
Recommendation:
It is recommended for young children, older adults, and individuals with certain medical conditions.
The Measles, Mumps, and Rubella (MMR) Vaccine protects against three highly contagious diseases: measles, mumps, and rubella.
The MMR vaccine is crucial for preventing these viral infections and their potential complications, such as severe respiratory problems, encephalitis, and birth defects.
Recommendation:
It is typically administered in two doses, with the first dose given between 12-15 months of age and the second dose between 4-6 years.
The Tdap vaccine is a combination vaccine that protects against three bacterial infections: tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis (whooping cough).
Tetanus causes severe muscle stiffness, diphtheria affects the throat and can lead to breathing difficulties, and pertussis is a highly contagious respiratory infection.
Recommendation:
It is typically given to adolescents and adults as a booster shot to maintain immunity against these diseases.
The HPV vaccine protects against several strains of the human papillomavirus, which can lead to various types of cancer, including cervical, anal, and oropharyngeal cancer.
Recommendation:
It is recommended for both males and females and is usually given as a series of two or three doses. The vaccine is most effective when administered before becoming sexually active, as it helps prevent HPV infection.
Hepatitis A is a viral infection that primarily affects the liver. It is typically transmitted through contaminated food, water, or close contact with an infected person.
Recommendation:
The hepatitis A vaccine is recommended for individuals who are at risk of hepatitis A infection or its complications. This includes children aged 12-23 months, individuals traveling to countries with high hepatitis A prevalence, individuals with chronic liver disease, and certain occupational groups, among others. Vaccination may also be recommended during outbreaks or for individuals with potential exposure to the virus.
The hepatitis B vaccine offers protection against the hepatitis B virus, which can cause liver inflammation, cirrhosis, and liver cancer.
Recommendation:
It is typically administered as a series of three or four doses, with the first dose given at birth or during early infancy. The vaccine is also recommended for individuals at higher risk of exposure, such as healthcare workers, individuals with multiple sexual partners, and those who inject drugs.
Rotavirus is a highly contagious virus that causes severe diarrhea, vomiting, and dehydration, particularly in infants and young children.
Recommendation:
Rotavirus vaccination is typically recommended as part of routine childhood immunizations. It is especially important for infants and young children, as they are most vulnerable to severe rotavirus gastroenteritis.
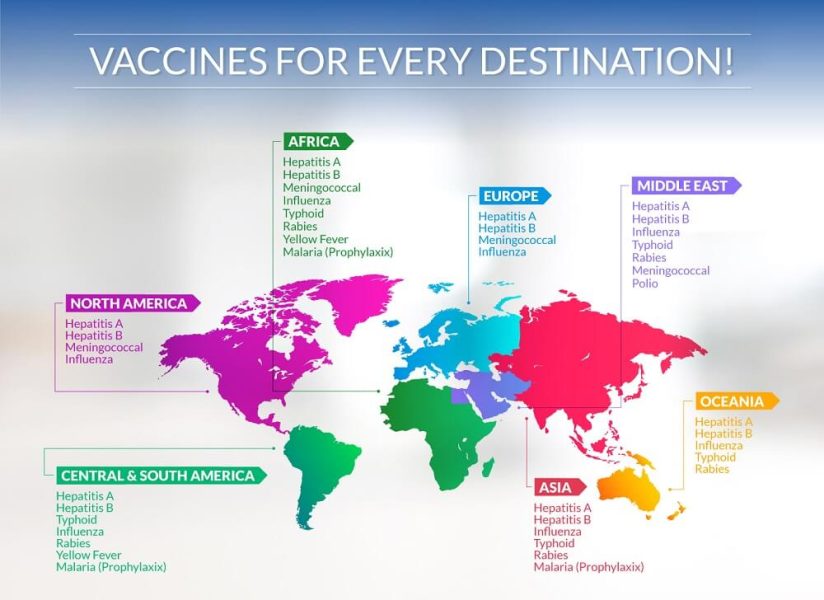
Travel Vaccinations:
When traveling to specific regions of the world, it is crucial for travelers to receive travel vaccinations. These vaccinations aid in safeguarding against infections like MMR, Hepatitis A/B, Typhoid, and others. Additionally, different locations may have distinct vaccination prerequisites based on local health conditions.
You can visit https://cdc.gov for more country specific information.
Protecting the health of our community is a shared responsibility.
Vaccination is a crucial step in safeguarding your health and preventing the spread of infectious diseases. Contact us to learn more about our vaccine services, availability and schedule an appointment to receive the necessary vaccinations.












 أنقر هنا
أنقر هنا أنقر هنا
أنقر هنا